<Back to Index>
This page is sponsored by:
PAGE SPONSOR
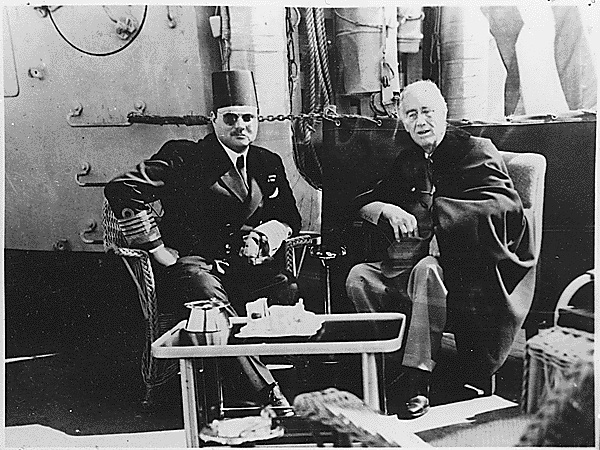


Farouk I of Egypt (Arabic: فاروق الأول Fārūq al-Awwal) (11 February 1920 18 March 1965), was the tenth ruler from the Muhammad Ali Dynasty and the penultimate King of Egypt and the Sudan, succeeding his father, Fuad I of Egypt, in 1936.
His full title was "His Majesty Farouk I, by the grace of God, King of Egypt and Sudan, Sovereign of Nubia, of Kordofan, and of Darfur." He was overthrown in the Egyptian Revolution of 1952 and forced to abdicate in favor of his infant son Ahmed Fuad, who succeeded him as Fuad II of Egypt. He died in exile in Italy.
His sister Princess Fawzia Fuad was the first wife and Queen Consort of the Shah of Iran Mohammad Reza Pahlavi.
As Crown Prince, Farouk held the rank of First Scout of Egypt.
The great - great - grandson of Muḥammad Alī, Farouk was of Albanian descent as well as native Egyptian and Turkish descent through his mother Queen Nazli Sabri. Before his father's death, he was educated at the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, England. Upon his coronation, the 16 year old King Farouk made a public radio address to the nation, the first time a sovereign of Egypt had ever spoken directly to his people in such a way:
| | And if it is God's will to lay on my shoulders at such an early age the responsibility of kingship, I on my part appreciate the duties that will be mine, and I am prepared for all sacrifices in the cause of my duty... My noble people, I am proud of you and your loyalty and am confident in the future as I am in God. Let us work together. We shall succeed and be happy. Long live the Motherland! | |
Farouk was enamored of the glamorous royal lifestyle. Although he already had thousands of acres of land, dozens of palaces and hundreds of cars, the youthful king often traveled to Europe for grand shopping sprees, earning the ire of many of his subjects. It is said that he ate 600 oysters a week. In 1951, he bought the pear shaped 94 - carat Star of the East Diamond and a fancy - colored oval - cut diamond from jeweler Harry Winston. By the time of the King's overthrow in 1952, Winston had still not received payment for the two gems; but, three years later, an Egyptian government legal board entrusted with the disposal of the former royal assets, ruled in his favor. Nevertheless, several years of litigation were needed before he was able to reclaim the Star of the East from a safe deposit box in Switzerland.
He was most popular in his early years and the nobility largely celebrated him. For example, during the accession of the young King Farouk, "the Abaza family had solicited palace authorities to permit the royal train to stop briefly in their village so that the king could partake of refreshments offered in a large, magnificently ornamented tent the family had erected in the train station."
Farouk's accession initially was encouraging for the populace and nobility, due to his youth and Egyptian roots through his mother Nazli Sabri. However, the situation was not the same with some Egyptian politicians and elected government officials, with whom Farouk quarreled frequently, despite their loyalty in principle to his throne.
During the hardships of Second World War, criticism was leveled at Farouk for his lavish lifestyle. His decision not to put out the lights at his palace in Alexandria, during a time when the city was blacked out because of German and Italian bombing, was deemed particularly offensive by Egyptian people. Owing to the continuing British occupation of Egypt, many Egyptians, Farouk included, were positively disposed towards Germany and Italy, and despite the presence of British troops, Egypt remained officially neutral until the final year of the war. Consequently, the royal Italian servants of Farouk were not interned, and there is an unconfirmed story that Farouk told British Ambassador Sir Miles Lampson (who had an Italian wife), "I'll get rid of my Italians when you get rid of yours". In addition, Farouk was known for harboring certain Axis sympathies and even sending a note to Hitler saying that an invasion would be welcome. Farouk declared war on the Axis Powers only under heavy British pressure in 1945, long after the fighting in Egypt's Western Desert had ceased.
Following a ministerial crisis in February 1942, the British government, through its ambassador in Egypt, Sir Miles Lampson, pressed Farouk to have a Wafd or Wafd - coalition government replace Hussein Sirri Pasha's government. On the night of 4 February 1942, British troops and tanks surrounded Abdeen Palace in Cairo and Lampson presented Farouk with an ultimatum. Farouk capitulated, and Nahhas formed a government shortly thereafter. However, the humiliation meted out to Farouk, and the actions of the Wafd in cooperating with the British and taking power, lost support for both the British and the Wafd among both civilians and, more importantly, the Egyptian military.
Farouk is also reported as having said "The whole world is in revolt. Soon there will be only five Kings left - the King of England, the King of Spades, the King of Clubs, the King of Hearts, and the King of Diamonds."
Farouk was widely condemned for his corrupt and ineffectual governance, the continued British occupation, and the Egyptian army's failure to prevent the loss of 78% of Palestine to the newly formed State of Israel in the 1948 Arab - Israeli War. Public discontent against Farouk rose to new levels. In the CIA, the project to overthrow King Farouk, known internally known as "Project FF [Fat Fucker]", was initiated by CIA operative Kermit Roosevelt, Jr. The CIA was disappointed in King Farouk for not improving the functionality and usefulness of his government and had actively supported the toppling of King Farouk by the Free Officers. Finally, on 23 July 1952, the Free Officers Movement under Muhammad Naguib and Gamal Abdel Nasser staged a military coup that launched the Egyptian Revolution of 1952. Farouk was forced to abdicate, and went into exile in Monaco and Italy where he lived for the rest of his life. Immediately following his abdication, Farouk's baby son, Ahmed Fuad, was proclaimed King Fuad II, but for all intents and purposes Egypt was now governed by Naguib, Nasser and the Free Officers. On 18 June 1953, the revolutionary government formally abolished the monarchy, ending 150 years of the Muhammad Ali dynasty's rule, and Egypt was declared a republic.
The revolutionary government quickly moved to auction off the King's vast collection of trinkets and treasures. Among the more famous of his possessions was one of the rare 1933 Double Eagle coins, though the coin disappeared before it could be returned to the United States (it later reappeared in New York in 1996 and was eventually sold at auction for over seven million dollars).
Farouk fled Egypt in great haste, and his abandoned possessions including a huge collection of pornography became an object of curiosity and ridicule. On his exile from Egypt, Farouk settled first in Monaco, and later in Rome, Italy. On 29 April 1958, the United Arab Republic, a federation of Egypt and Syria issued rulings revoking his citizenship. He was granted Monegasque citizenship in 1959 by his close friend Prince Rainier III.
The blue - eyed Farouk was thin early in his reign, but later gained an enormous amount of weight. His taste for fine cuisine made him dangerously obese, weighing nearly 300 pounds (136 kg) an acquaintance described him as "a stomach with a head". He died in the Ile de France restaurant in Rome, Italy on 18 March 1965. He collapsed and died at his dinner table following a characteristically heavy meal. While some claim he was poisoned by Egyptian Intelligence, no official autopsy was conducted on his body. His will stated that his burial place should be in the Al Rifa'i Mosque in Cairo, but the request was denied by the Egyptian government under Gamal Abdel Nasser, and he was going to be buried in Italy. King Faisal of Saudi Arabia stated he would be willing to have King Farouk buried in Saudi Arabia, upon which President Nasser agreed for the former monarch to be buried in Egypt, not in the Mosque of Al Rifai' but in the Ibrahim Pasha Burial Site.
A likely apocryphal story about Farouk's lavish living in exile was that he refused to donate money to relieve poverty on the basis that "If I donate my fortune to buy food, all of Egypt eats today, eats tomorrow, and the day after that they are starving once again", thus rationalizing his high living.
In addition to an affair with the British writer Barbara Skelton, among numerous others, Farouk was married twice, with a claim of a third marriage. His first wife was Safinaz Zulficar (1921 1988), the daughter of Youssef Zulficar Pasha. Safinaz was renamed Farida upon her marriage. They were married in 1938, and divorced in 1948, producing three daughters.
Farouk's second wife was a commoner, Narriman Sadek (1934 2005). They were married in 1951, and divorced in 1954, having only one child, the future King Fuad II.
While in exile in Italy, Farouk met Irma Capece Minutolo, an opera singer, who became his companion. In 2005, she claimed that she married the former King in 1957.
The ostentatious king's name is used to describe imitation Louis XV style furniture known as "Louis - Farouk". The imperial French style furniture became fashionable among Egypt's upper classes during Farouk's reign so Egyptian artisans began to mass - produce it. The style uses ornate carving, is heavily gilded, and is covered in elaborate cloth. The style, or imitations thereof, remains widespread in Egypt.
King Farouk amassed one of the most famous coin collections in history which included an extremely rare American Gold Minted 1933 Double Eagle coin and (non concurrently) two 1913 Liberty Head nickels.
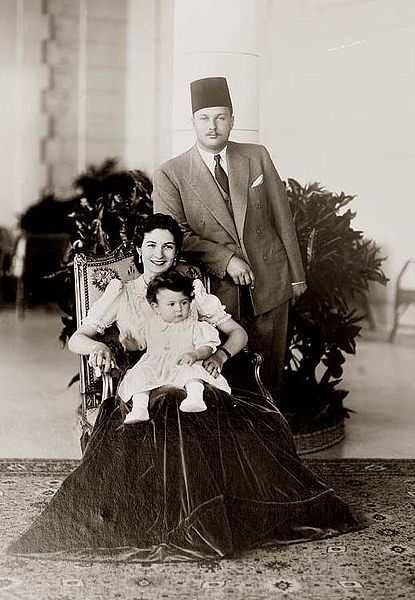
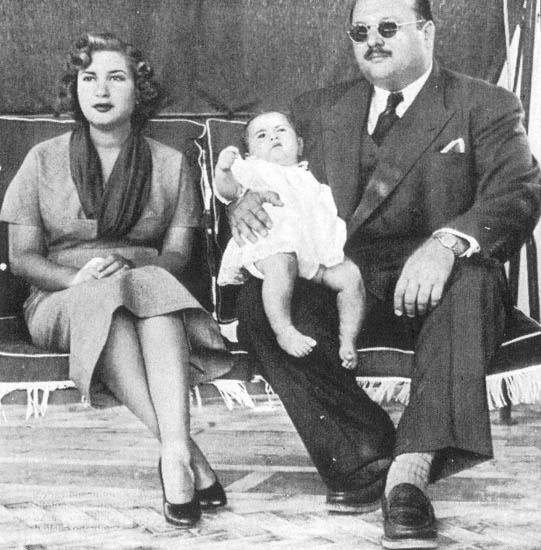


Fuad II (Arabic: فؤاد الثاني) (born 16 January 1952 as Prince Ahmad Fuad) was the last King of Egypt and Sudan.
He ascended the throne on 26 July 1952 upon the abdication of his father King Farouk I following the Egyptian Revolution of 1952. Farouk had hoped that his abdication would appease the revolutionaries and other anti - royalist forces, and that his son could serve as a unifying force for the country. However, the infant king reigned for less than a year until 18 June 1953, when Egypt was declared a republic. Fuad II was the eleventh and last monarch of the Muhammad Ali Dynasty, which had ruled Egypt (and later Sudan) since 1805. His name is sometimes spelled Fouad.
Fuad was less than a year old at the time of his accession to the throne, thus he was never formally crowned. Upon Farouk's abdication, the now former king was exiled, and the new King Fuad left Egypt with him and his family. The Council of Regency headed by Prince Muhammad Abdel Moneim formally represented Fuad in Egypt during his absence.
After being deposed, Fuad was brought to Switzerland, where he was raised. He later emigrated to Paris where he married and had his three children raised before returning to Switzerland after his divorce.
In 1976, the former king married Dominique - France Picard (née Loeb, born 1948), the daughter of Robert Loeb and his wife, Paule Picard. She converted to Islam and assumed the title Queen Fadila of Egypt. The couple had three children before they divorced in 1997.
Their children are:
- HRH Muhammad Ali, Prince of the Sa'id (born 5 February 1979)
- HRH Princess Fawzia-Latifa (born 12 February 1982)
- HRH Prince Fakhr Eddin (born 25 August 1987)
In May 2010, he recorded a television interview with "ON TV" talking about his visit to Egypt, and how he felt about the Egyptian people, and their view of his late father.